Did you know the DDG(X) program at Pascagoula represents the largest guided missile destroyer development in U.S. naval history, with capacities and capabilities set to redefine modern surface combatants? In a world where fast-evolving threats and cutting-edge technology collide, every decision—like building the DDG(X) in Mississippi—carries massive implications for America’s security, economy, and military future. This article dives deep into why the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard matters right now —from surprising engineering feats to local job creation, to its role in global power balance.
Surprising Numbers: The U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard and Its Unprecedented Scale
The U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard is a testament to unprecedented scale and ambition in American shipbuilding. With the U.S. Navy planning to invest billions over the coming decades, the DDG(X) program stands as the largest single-class surface combatant initiative since the Arleigh Burke program began. Pascagoula Shipyard, already famed for constructing past Arleigh Burke-class destroyers, is expected to expand operations further to accommodate these new generation large surface combatants. In fact, each new destroyer will stretch engineering and logistical capabilities to new levels, with the workforce, material throughput, and infrastructure needs dwarfing previous projects.
Beyond the financials, the magnitude is evident in man-hours and advanced technologies. The shipyard anticipates adding hundreds of highly skilled jobs while also investing in automation, digital engineering, and cutting-edge materials. The scale benefits not only the United States Navy but also the broader Gulf Coast community. As the DDG(X) sets new records for ship size, crew capacity, and combat system complexity, it underscores just how far guided missile destroyers have evolved from their Cold War predecessors. The ripple effect: new standards for safety, firepower, and technological integration in every surface combatant that leaves Pascagoula’s docks.
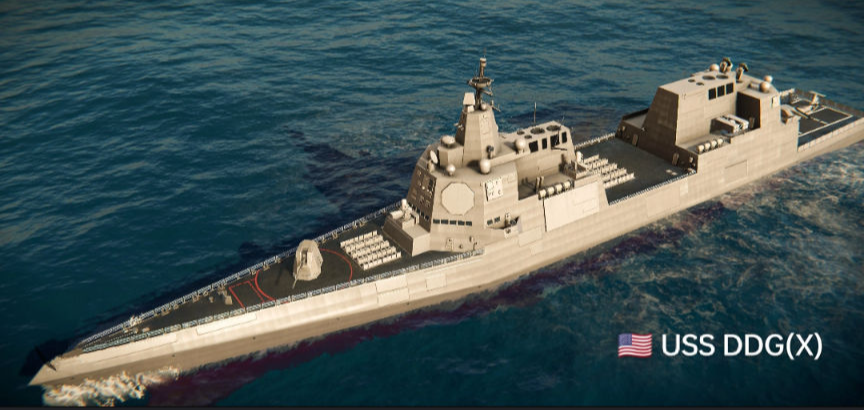

Why This Generation Large Surface Combatant Program Is a Game Changer
This new generation large surface combatant program—epitomized by the DDG(X)—marks a pivotal break from traditional naval design. Instead of incremental upgrades, the DDG(X) embraces a clean-sheet approach driven by both operational lessons (from Flight II and Flight III Arleigh Burke-class destroyers) and bold predictions for future threats. The program isn’t just scaling up—it’s transforming what a surface combatant can be. The DDG(X)’s modular architecture supports easier upgrades, while integrated power solutions and advanced weapon systems pave the way for next-generation missile defense.
What makes it even more groundbreaking is its role as a “platform for innovation,” prepared from inception to host future technologies such as unmanned systems, directed-energy weapons, and enhanced sea control capabilities. Notably, the U.S. Navy’s DDG(X) aims at outpacing potential adversaries, ensuring the Department of Defense maintains technological superiority in contested waters. This game-changing perspective reflects a unified vision between the Navy, Congress, and major contractors who understand surface combatants’ critical role in the U.S.’s military strategy.
Understanding the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard: Key Features and Ambitions
The U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard brings together the best of American engineering and design , fusing legacy experience from Arleigh Burke and Zumwalt classes with transformative new capabilities. Among its standout features are more advanced combat system architectures, multi-mission flexibility, and an upgraded propulsion system that supports integrated electric power for both sensors and emerging weapons. These innovations position the DDG(X) to tackle next-generation threats, from hypersonic missiles to increasingly complex cyber-attacks.
Underlying the design is a forward-thinking ambition: futureproofing. Rather than constructing another variant in a long line of iterative class destroyers, the Navy envisions the DDG(X) as a “digital backbone” for integrating technologies that might not yet exist. This modularity allows for cost-effective mid-life upgrades—essential when keeping pace with global adversaries’ rapidly evolving capabilities. With Pascagoula Shipyard’s proven pedigree, the partnership signals a new era for American surface combatant construction, focused on speed, adaptability, and overwhelming combat power.
How Ingalls Shipbuilding and Bath Iron Works Shape the Future of Guided Missile Destroyers
Two industrial titans anchor the DDG(X) future: Ingalls Shipbuilding in Pascagoula and Bath Iron Works in Maine. Each has decades of experience with Arleigh Burke and Zumwalt-class destroyers, but for the DDG(X), their collaboration and healthy competition drive key advances in productivity, innovation, and quality. Ingalls’ investments in automation, digital ship modeling, and high-tech fabrication are complemented by Bath’s renowned workmanship and legacy of iterative improvements in combat system integration.
Together, these yards are raising the bar for large surface combatant construction. Bath Iron Works brings lessons from “cold weather” builds and workforce management, while Ingalls Shipbuilding leads in modular assembly and logistics optimization. Their shared expertise ensures the DDG(X) is more than just another guided missile destroyer; it is a versatile, resilient platform tailored for both near-term deterrence and decades-long adaptability. This interplay underscores how collaboration between American shipbuilding powerhouses shapes not only national defense but the future of global sea control.
Flight III vs. Flight II: Evolution in Arleigh Burke-Class Destroyers
A crucial stepping stone to the DDG(X) can be seen in the transition from Flight II to Flight III Arleigh Burke-class destroyers . While Flight II improved upon the original Arleigh Burke by boosting weapon capacity and survivability, Flight III introduced a quantum leap in sensor and missile defense systems—most notably, the cutting-edge AN/SPY-6 radar and advanced power generation modules.
These improvements were not cosmetic—they elevated the Arleigh Burke to a level previously unimagined for surface combatants, paving the way for the even more ambitious design of the DDG(X). Every piece of feedback from crews and commanders operating Flight II and III destroyers informed the design of the DDG(X), from weapon system layout to integration with unmanned systems. The DDG(X) distills these lessons, ensuring next-generation destroyers can dominate in future high-threat environments.
Why Ingalls Shipbuilding in Pascagoula Is Essential for U.S. Navy's Surface Combatants
Ingalls Shipbuilding in Pascagoula has long been a cornerstone of the United States Navy’s surface combatant force, building more Arleigh Burke-class destroyers than any other yard. As the U.S. Navy turns its focus to the DDG(X), Ingalls’ expertise in assembling complex, modular hulls and integrating advanced weapon and combat systems becomes ever more vital. Their shipyard’s unique infrastructure—massive covered assembly halls, state-of-the-art dry docks, and proximity to deep-water routes—means a faster build schedule and more robust quality control.
But the value of Ingalls Shipbuilding goes beyond steel and sensors. Its workforce—one of the most experienced in the U.S.—delivers continuous process improvement, safety, and technical innovation. Partnering with Bath Iron Works and Newport News Shipbuilding in Virginia, Ingalls guarantees redundancy and ensures that fleet modernization remains on schedule regardless of global disruptions. In short, Pascagoula doesn’t just build ships; it builds the strong, adaptable surface combatants the Navy needs for both present and future power projection.
The Strategic Role of Pascagoula Shipyard in Large Surface Combatant Construction
The Pascagoula Shipyard’s strategic location on the Gulf Coast isn’t just about geography—it’s about access to talent, materials, and rapid delivery channels to Atlantic and Pacific theaters. As one of only a handful of U.S. shipyards capable of building large surface combatants, Pascagoula provides critical redundancy in America’s ship construction capability.
Moreover, the shipyard’s continuous modernization enables the swift adoption of digital engineering, automation, and robotics. These investments enable more efficient construction schedules and reduce the chance of bottlenecks—a crucial advantage as the Navy seeks to maintain a competitive edge. For the DDG(X), this means faster delivery of destroyers that have higher survivability, stronger offensive and defensive suites, and unparalleled adaptability. The Pascagoula Shipyard’s role is thus not just operational; it’s existential for a continuously modernized Navy ready for the challenges ahead.

Collaboration Across Shipyards: Newport News, Bath Iron, and Ingalls
The magnitude of the DDG(X) project requires a coalition of expertise. Newport News Shipbuilding, while renowned for nuclear carriers and submarines, has contributed vital lessons on large vessel logistics, modular construction, and cross-program integration. Bath Iron Works brings its unique combination of heritage, Northern workforce tenacity, and proven track record. Ingalls Shipbuilding binds it all together with its focus on efficiency and rapid turnaround for surface combatants.
This collaborative environment is unprecedented in its transparency and data-sharing, leveraging digital twins and virtual integration to eliminate costly errors before steel is ever cut. By blending strengths from all three shipyards, the Navy ensures its guided missile destroyers are second-to-none in capability, cost control, and long-term survivability. The synergy between these shipbuilding giants is a force multiplier for the entire Department of Defense.
The Legacy of the Arleigh Burke-Class Destroyer and Pascagoula’s New Chapter
No discussion about the DDG(X) is complete without acknowledging the storied legacy of the Arleigh Burke-class destroyer , which has set the gold standard for 21st-century surface combatants. Arleigh Burke-class ships have proven themselves as reliable, multi-mission guided missile platforms capable of missile defense, sea control, and forward power projection. Pascagoula Shipyard’s role in delivering so many of these class destroyers cemented its reputation as an essential player in national defense.
Now, as Pascagoula takes the helm for the DDG(X), it steps into a new chapter defined by innovation and ambition. Lessons learned from decades of building and modernizing Arleigh Burke-class destroyers are manifest in every aspect of the DDG(X)—from propulsion choices to the layout of advanced weapon systems. This transition embodies more than ship construction: it’s about the evolution of American sea power itself.
Missile Defense Advancements in the DDG(X) Class Destroyer
Missile defense isn’t an add-on for the DDG(X); it’s core to the program’s mission. The DDG(X) will field larger and more advanced Vertical Launch Systems (VLS) than even the Flight III destroyer, supporting future-standard hypersonic interceptors and cooperative missile tracking with other ships, aircraft, and satellites. Innovations like integrated electric power and digital combat system architectures enable seamless upgrades to missile defense capabilities, ensuring these surface combatants can protect the fleet and allied interests against the most sophisticated threats.
Improved radar signatures, longer-range sensor reach, and real-time data fusion mean each new destroyer serves as a floating command-and-control hub. As American adversaries deploy faster and stealthier missiles, the DDG(X) ensures U.S. Navy task forces remain protected, making a profound difference in the balance of deterrence around the world.
From Flight II to DDG(X): Lessons Learned and Innovations
The shift from Flight II and Flight III Arleigh Burke-class destroyers to DDG(X) is the result of a continual process of feedback and forward-looking design thinking. Engineers absorbed decades of operational learning—crew workload, maintenance logistics, adaptability to new technologies—and embedded these insights within the DDG(X) blueprint. Innovations such as open-architecture computing, “plug-and-play” weapon systems, and enhanced power management stem directly from real-world experience managing aging class destroyers.
Even more, unmanned systems integration and cyber-resilience features offer flexibility for future operational concepts, from distributed lethality to autonomous minehunting and multi-domain warfare. As the U.S. Navy pivots towards fighting in contested, high-tech environments, the lessons and innovations baked into DDG(X) provide a critical leap forward.
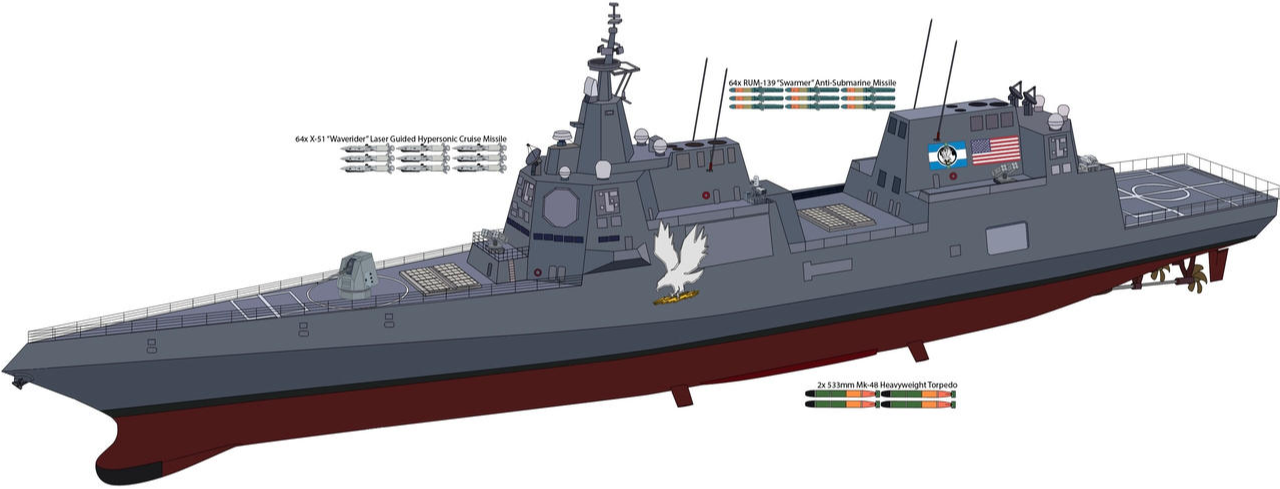
Why the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard Matters in the Current Geopolitical Climate
Global tensions are on the rise, with rivals rapidly investing in blue-water navies and next-generation weapon systems. In this context, the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard is not merely a procurement project—it is a frontline investment in American security and global stability. Advanced surface combatants like the DDG(X) provide the flexibility and firepower required for sea control missions, joint force projection, and robust regional deterrence.
As the Department of Defense recalibrates military strategy for the Pacific, Atlantic, and Arctic, the need for survivable, adaptable, and technologically superior guided missile ships is greater than ever. Pascagoula’s DDG(X) ensures fleet commanders have the best possible tools for missile defense, anti-submarine warfare, and ensuring American allies can operate with confidence in contested oceans. In today’s fraught geopolitical climate, the tangible presence of the DDG(X) program is a signal of resolve that adversaries cannot ignore.
Opinion: The Critical Role of Guided Missile Capability for National Defense
In my view, there has never been a more decisive moment for American investment in guided missile capability. The DDG(X), as a new flagship surface combatant, does more than defend ships against air, surface, and subsurface threats—it projects willpower and decisiveness on the global stage. The ability to integrate missile defense with offensive punch offers the Navy and the nation powerful new options for both deterrence and dominance.
As adversaries aim to outpace our naval forces with hypersonic advancements and novel attack platforms, only a dynamic, forward-thinking program like DDG(X) can keep the U.S. Navy ahead. It is not an exaggeration to say that the future of American sea power hinges on maintaining this technological and operational edge.
What the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard Means for Local and National Economy
Beyond its strategic importance, the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula shipyard is an economic engine for both Mississippi and the nation. Ingalls Shipbuilding, a major contractor, employs thousands of skilled tradespeople, engineers, and support staff, with the DDG(X) set to create even more high-quality jobs. Each destroyer fuels a network of hundreds of suppliers—from advanced electronics in California to steel fabrication in Pennsylvania—showcasing the scale of technology transfer and regional impact.
Local businesses benefit from the influx of skilled workers and increased demand for services, while community colleges and technical institutions partner with Ingalls Shipbuilding to develop the next generation of shipbuilders. Nationally, the ripple effect reaches even further as innovations in digital engineering move from military to civilian sectors. The DDG(X) program, therefore, stands as both a driver of U.S. economic strength and an incubator for technological advances that benefit the entire country.

Jobs, Technology Transfer, and Regional Impact
The Pascagoula region, home to a diverse and resilient workforce, experiences profound effects from any upgrade in shipyard activity. The DDG(X) project is set to bolster the local economy through job creation , provide technological upskilling opportunities, and promote regional supplier growth. Local partnerships with universities and tech startups bring fresh innovations to defense manufacturing, enhancing productivity and competitiveness.
Technology transfer is especially notable: digital shipbuilding tools and process engineering developed for DDG(X) soon filter into civilian industries, driving broader economic gains. From precision welding robots to augmented-reality maintenance applications, the region becomes a hub for both current and future tech talent. Economic diversity, coupled with robust support from government and industry, ensures the ongoing prosperity of Pascagoula and surrounding communities.
-
Direct employment of thousands of skilled shipbuilders and engineers
-
Technology transfer into civilian manufacturing and logistics
-
Boost to regional suppliers across dozens of states
-
Local investments in education, training, and infrastructure
-
Enhanced tax base for local communities and Mississippi as a whole
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparison: U.S. Navy's DDG(X), Flight II & III Arleigh Burke, and Existing Large Surface Combatants |
|
Class/Ship |
Primary Role |
Displacement (tons) |
Missile Cells |
Main Radar |
Notable Tech |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DDG(X) |
Next-gen guided missile destroyer, multi-domain warfare |
13,000+ (projected) |
128+ (expandable/modular) |
Future scalable radar/3D arrays |
Integrated electric drive, digital architecture, hypersonic missile defense |
|
Arleigh Burke Flight III Destroyer |
Advanced air/missile defense, multi-mission |
9,700 (full load) |
96 |
AN/SPY-6 AESA |
Improved power, open systems combat suite |
|
Arleigh Burke Flight II Destroyer |
Multi-mission, legacy missile defense |
8,900 (full load) |
90 |
AN/SPY-1D |
Proven, upgradable but less modular |
|
Ticonderoga Cruiser |
Command/control, air defense |
9,600 (full load) |
122 |
AN/SPY-1A/B |
Aging, limited flexibility for upgrades |
Quotes from Naval Experts and Industry Leaders on the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard
"DDG(X) is not just a replacement—it’s a generational leap for American naval power. Pascagoula’s geographic advantages, proven workforce, and commitment to innovation make it the ideal home for this critical program."
— Shipbuilding Executive, Ingalls Shipbuilding Division
"Guided missile destroyers have always been the backbone of U.S. sea power. The DDG(X) amplifies this legacy, giving our commanders unmatched flexibility and punch for tomorrow’s threats."
— National Security Analyst, Defense Policy Forum
FAQs About the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard
How is the DDG(X) different from existing guided missile destroyers?
The DDG(X) is a leap ahead in every major function: more modular construction for easier upgrades, greater missile capacity, integrated power systems for future technologies, and improved survivability against modern threats. Unlike Flight II and Flight III Arleigh Burke destroyers, DDG(X) is built with a digital backbone, supporting next-gen radar, hypersonic missile defense, and rapid adaptation to new operational needs.
What is the timeline for delivery of the first DDG(X)?
The first DDG(X) is expected to begin major construction at Pascagoula in the late 2020s, with delivery projected in the early 2030s. This timeline allows for thorough testing, integration of the newest combat and weapon systems, and careful coordination with parallel builds at Bath Iron Works. The Navy remains committed to delivering a fully operational and future-ready surface combatant on schedule.
Why was Pascagoula chosen for building the next generation large surface combatant?
Pascagoula offers unique advantages: a skilled workforce, state-of-the-art facilities, proximity to suppliers, and a tradition of delivering on large surface combatant contracts. Its experience building Arleigh Burke-class destroyers provides the foundation for tackling the technical challenges of DDG(X). The shipyard’s location, infrastructure, and collaborative partnerships made it the logical—and strategic—choice for the DDG(X) flagship program.
People Also Ask: Why Is the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard Generating Attention?
How does the DDG(X) impact U.S. missile defense and strategic deterrence?
The DDG(X) extends U.S. missile defense capability by incorporating larger Vertical Launch Systems, new sensors, and integrated combat systems that can engage incoming threats faster and with higher precision. By hosting leading-edge missile interceptors and supporting cooperative engagement with other platforms, DDG(X) strengthens both national defense and deterrence across contested regions.
What sets Ingalls Shipbuilding and Bath Iron Works apart in the naval defense sector?
Both Ingalls Shipbuilding and Bath Iron Works combine a legacy of proven reliability with a forward-looking approach to innovation. Ingalls excels in modular ship construction and rapid delivery, while Bath brings deep expertise in combat system integration and workforce training. Together, they form the industrial backbone for next-generation surface combatants and are trusted partners to the United States Navy and Department of Defense.

Future Prospects: Will the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard Set the Standard for Surface Combatants?
The eyes of the world are on Pascagoula and the United States as the DDG(X) prepares to set sail. With its unmatched blend of scalability, firepower, and adaptability, this guided missile destroyer is likely to become the global benchmark for future large surface combatants. For allies, it sets a new model of technological excellence; for adversaries, a warning to pace with America’s next-generation capabilities or fall behind. International navies are closely watching the DDG(X) program, with many poised to study or even emulate its key design concepts for their own fleets.
Opinion: Long-Term Value and International Implications for Naval Power
In my opinion, the DDG(X) at Pascagoula exemplifies long-term value not just for the U.S. Navy, but for the global coalition of democratic maritime powers. As a platform, it supports flexible engagement strategies, evolves alongside ever-changing threats, and serves as a visible commitment to defending a rules-based international order. The impact of the DDG(X) will ripple far beyond Pascagoula, shaping naval architecture, industry standards, and power relationships well into the mid-21st century.
Key Takeaways: The Strategic and Economic Importance of the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula
-
DDG(X) represents a generational leap for U.S. missile destroyer capability and surface combatant design.
-
Ingalls Shipbuilding in Pascagoula is essential, leveraging workforce experience and cutting-edge facilities.
-
Collaboration with Bath Iron Works and Newport News ensures resilience, innovation, and timely delivery.
-
Economic ripple effects benefit local workers, suppliers, and national technology advancement.
-
The DDG(X) confronts today’s threats as an adaptable platform for future innovations and unmanned systems.
-
Pascagoula’s new chapter positions the U.S. for military and economic leadership on the world stage.
Ready to Learn More or Partner With Leaders in U.S. Naval Innovation?
Connect with Gulf Coast technology and shipbuilding experts
Interested in the innovations driving the U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard? Whether you’re seeking partnership opportunities, technical insights, or career pathways, Gulf Coast leaders are ready to connect.
-
Visit Gulf Coast Tech for the latest program updates and industry news.
-
Engage with local educational partners to explore training in shipbuilding technology or digital engineering.
-
Check out careers and supplier opportunities through Ingalls Shipbuilding and Bath Iron Works websites.
-
Attend industry forums or webinars to stay informed and network with defense innovation leaders.
Further Reading and Author's Final Thoughts
The U.S. Navy's DDG(X) at Pascagoula Shipyard is more than a maritime milestone—it’s the future in motion. Stay ahead of the curve; follow this program as it shapes the next chapter of American and international naval excellence.
The U.S. Navy’s DDG(X) program at Pascagoula Shipyard represents a significant advancement in naval warfare capabilities. HII’s Ingalls Shipbuilding division in Pascagoula, Mississippi, has been awarded a design engineering contract for the DDG(X), marking a pivotal step in developing the next-generation guided-missile destroyer. ( hii.com ) This initiative underscores the shipyard’s critical role in enhancing the Navy’s surface combatant fleet.
In addition to the DDG(X) program, Ingalls Shipbuilding has been actively involved in modernizing existing vessels. Notably, the USS Zumwalt (DDG-1000) underwent significant upgrades at the Pascagoula facility, including the integration of the Conventional Prompt Strike weapon system, ensuring it remains one of the most technologically advanced ships in the Navy. ( hii.com )
These developments highlight Pascagoula Shipyard’s strategic importance in advancing naval technology and maintaining the United States’ maritime superiority.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment